MEET NEXPLANON
the birth control implant that goes
in your arm
How NEXPLANON Worksalready on NEXPLANON?
Get a refresher on NEXPLANON and learn what comes next.
What’s Next

NEXPLANON works by preventing ovulation
NEXPLANON works by using a hormone that stops an egg from being released by your ovary and prevents sperm from reaching the egg. It also changes the lining of your uterus.
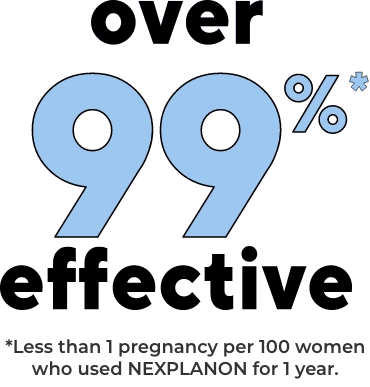

NEXPLANON is just as effective as the pill - without the daily hassle
This is birth control you don’t have to take every day. The small, flexible implant prevents pregnancy for up to 3 years.*
*NEXPLANON must be removed by the end of the third year.

it's reversible
NEXPLANON is reversible. If your plans change, it can be removed by a trained healthcare professional at any time during the 3-year period.
side effects of NEXPLANON
The most common side effect of NEXPLANON is a change in your normal menstrual bleeding pattern. In studies, 1 in 10 women stopped using NEXPLANON because of an unfavorable change in their bleeding pattern. Besides changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, other frequent side effects that caused women to stop using the implant include mood swings, weight gain, headache, acne, and depressed mood.
questions to talk through with your doctor
Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of NEXPLANON.
Yes, NEXPLANON is a small (about the size of a matchstick), thin, and flexible birth control implant that provides 3 years* of continuous pregnancy prevention. It’s placed discreetly just under the skin on the inner side of your non-dominant upper arm by a trained healthcare professional.
*NEXPLANON must be removed by the end of the third year.
No, it's not an intrauterine device (IUD). It is an implant that is placed in your arm. Like an IUD, it's a long-acting birth control option. NEXPLANON lasts for 3 years.*
*NEXPLANON must be removed by the end of the third year.
NEXPLANON is 1.6 inches (4 centimeters) in length, about the size of a matchstick.
NEXPLANON is a hormone-releasing birth control implant for use by women to prevent pregnancy for up to 3 years.*
NEXPLANON prevents pregnancy in several ways. The most important way is by stopping the release of an egg from your ovary. NEXPLANON also thickens the mucus in your cervix and this change may keep sperm from reaching the egg.
NEXPLANON also changes the lining of your uterus.
*NEXPLANON must be removed by the end of the third year.
NEXPLANON is over 99% effective (less than 1 pregnancy per 100 women who used NEXPLANON for 1 year) at preventing pregnancy. NEXPLANON is one of the most effective forms of birth control available.
A trained healthcare professional can remove the implant at any time within the 3-year period. You may become pregnant as early as the first week after removal of the implant. If you do not want to get pregnant after removal of the NEXPLANON implant, you should start another birth control method, such as condoms, immediately.
Implant not actual size
